There's a lot of industry posturing and debate about software-defined networking (SDN). Most of it is academic, which is unfortunate for users who want to understand what SDN can really help them do and to see real-world examples of it in action. Enterprises want the ability to run their own private clouds, offer self-service networking capabilities to tenants, provide isolated and secure networks, and simplify the integration of company acquisitions.
Microsoft's SDN operates Azure, Office365, and 200 other cloud services across more than 1 million servers for hundreds of millions of customers. Azure has tens of thousands of network changes every day, so "Big SDN" is living and breathing in our cloud. Lessons learned from this experience can help demystify SDN and provide some guidance about how to make it possible in your own data center.
I'll spell out the top best practices in a series of blogs to show you how you can meet the common business goals that SDN is trying to achieve: agility, so the business can be flexible and grow with its customers' needs; efficiency, in order to provide the lowest possible cost of ownership; and predictability through reliable SLAs between key stakeholders.
SDN step by step
Though this statement may seem obvious, I recommend setting and achieving your SDN goals one at a time, rather than trying to change multiple networking capabilities in a single project. It would be nice just to turn on your SDN management solution and have it aggregate your networking resources, standardize your configurations, expand your network's capacity, maximize scale, increase performance, provide automation, ensure tenant isolation, improve workload mobility, cut operational complexity, reduce costs, and cure world hunger. But the reality is that you will be setting yourself up for failure.
The network is like the central nervous system of the data center, because it provides the communication fabric for its members to function together as a unified yet distributed system. An essential component of SDN is a highly available, centralized brain for the system. This is provided by SDN management software.
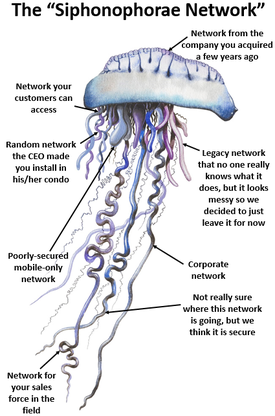
Today I see many customers with segmented networks and multiple administrative tools for each of their different networking devices. In the animal world, a colony of separate organisms that appear to function as a large single animal is called a siphonophorae, such as the jellyfish-like creature known as the Portuguese man-of-war. But just like the man-of-war, if one of the network segments breaks down, the entire solution will gradually cease to function. If you have ever had to restore a service after a distributed networking outage, you will probably wish you were swimming with the man-of-war instead of struggling with miles of networking cables.
One of the first goals should be to deploy SDN management and pool your networking resources so they can be software-controlled. This SDN management software can centrally govern your devices, such as switches, load balancers, or even gateway servers. This may involve adding every networking device to the software individually, or even controlling the current management system of those networking resources, so that your SDN software becomes a "manager of managers."
Test this configuration for a while until you can control the necessary networking devices in your data center from this software. Then you can start thinking about the next goal, whether that is standardization, high availability, automation, self-service, or multi-tenancy.
Now that you are on the journey toward SDN, you should also be extra selective when purchasing network devices. Ensure that the component can be controlled through a programmatic interface (API) such as REST, OMI, or SNMP. This will allow the SDN management software to control that device automatically, which can free up time for the IT department while reducing human error.
To summarize today's lesson, Symon says to set clear goals, take them one at a time, and don't be a siphonophorae. Next, I will discuss the biggest internal challenges that lie ahead on your journey to SDN.